Josiah Wedgwood (1769-1843) was the second son and namesake of the famous potter and inventor, Josiah Wedgwood (1730-95). He followed his father as head of the family’s pottery manufacturing firm, based at Etruria near Stoke-on-Trent. Although he was the second son and had lived as a country gentleman in Dorset before his father’s death, taking little interest in the business, its management fell to him because of his older brother’s ‘chronic incompetence’ and his younger brother’s death.
Tag: Etruria
Friday NewsDesk
We have spent most of the week reorganising our filing system and image archive. Several new posts have been put on this site. They include details of services provided by Staffordshire Library and a video about the Armstrong Whitley Bomber.

The Whitley was a Second World War heavy bomber. Built in Coventry, the Whitley was designed by John Lloyd, who grew up in Etruria. Other aircraft designed by John included the experimental flying wing, which ushered in the jet age and helped to create the V Bomber force and Concorde
Sir Morien Morgan, the Director of the Royal Aircraft Establishment at Farnborough, said John was one of the 20th century’s leading aeronautical engineers.
John is regarded as one of the 20th century’s leading aircraft designers.
Stoke-on-Trent, the city where he received his education and served an apprenticeship, has refused to recognise his achievements.
We hope you have a relaxing and enjoyable weekend. Take care. We will see you again on Monday.
The Armstrong Whitley Bomber
Did you know that the Armstrong Whitley Bomber was designed by John Lloyd, who grew up in Etruria? He was educated at Hanley High School. When John left school, he became an apprentice at Shelton Bar. During the First World War, he worked at the Royal Aircraft Factory. When the war ended, John went to work for Armstrong Whitworth, becoming the company’s chief aircraft designer in the 1920s.
Tunstall in the 1790s
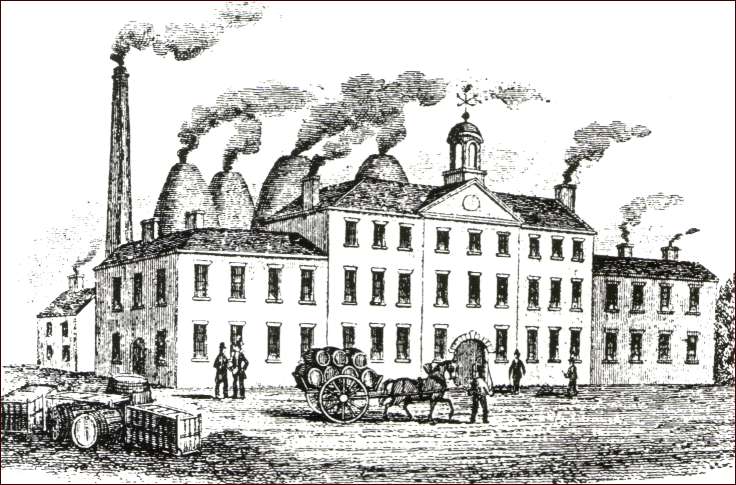
The sketch above shows William Adams’ Greengates Pottery in Tunstall. The factory built between 1779 and 1781 was one of the largest in the Potteries. It manufactured tableware, stoneware and jasper ornaments for the luxury market. William Chaffer, the author of ‘Marks and Monograms on Pottery and Porcelain’, said some of the jasper made at Greengates was ‘equal to, if not superior’ to that produced by Josiah Wedgwood at Etruria.
A Description of the Country From Thirty to Forty Miles Round Manchester, a book published in 1795, was compiled by Dr John Aikin. The book tells us about Newcastle-under-Lyme and North Staffordshire’s pottery towns and villages in the 1790s.
This edited extract from the book describes Tunstall as it was in the 1790s.
Tunstall is the pleasantest village in the Potteries. It stands on high ground, commanding extensive views of the surrounding countryside. Pottery manufacturers in the village produce good-quality ware and do considerable business. There was a church here, and human bones have been dug up. But such is the effect of time that no trace of either the church or the bones remains today. A small chapel has recently been built here. There is a considerable number of brick and tile works. They use local clay to make blue bricks, which look as well on the roofs of houses as moderate slate. Tunstall is four miles from Newcastle-under-Lyme and nine miles from Congleton. The turnpike road from Lawton to Newcastle-under-Lyme runs through Tunstall, where the turnpike road to Bosley in Cheshire begins [near the Wheatsheaf Inn].
Etruria Industrial Museum
This video showcases Etruria Industrial Museum. The museum is housed in a 19th century steam powered potter’s bone and flint mill. Built in 1857, the mill is a Grade II* listed building.
The museum is at Etruria Junction, where the Caldon Canal joins the Trent & Mersey Canal.
There is a statue of James Brindley (1716–1772) at the junction, which was the site of Etruria Wharf. A tramway ran from the wharf to Hanley/City Centre. The site of Stoke-on-Trent’s first public hospital is near the museum. Built in 1803, the hospital was called the Dispensary and House of Recovery.
Sir Smith Child (1808-1896)

A portrait of Sir Smith Child painted by John Nash Peake.
During the 19th century, Sir Smith Child was the most generous philanthropist in North Staffordshire. He used his vast wealth to support hospitals, build schools and churches, fight poverty and help handicapped children.
Although many historians think that his family name was Smith Child, it wasn’t. Smith was his Christian name and Smith was his surname. Smith Child was born at Newfield Hall, Tunstall, on 5 March 1808. His grandfather was Admiral Smith Child, who was a partner in Child & Clive. The firm owned Newfield Pottery and Clanway Colliery, where it mined coal and ironstone.
Smith’s parents were John George and Elizabeth Child, née Parsons. When his father died in 1811, he became heir to the Newfield estate and other estates owned by his grandfather.
Smith was educated at St. John’s College, Cambridge.
On 28 January 1835, he married Sarah Hill, an heiress, at Fulford Church. The couple had three children – two boys and a girl. The family lived at Newfield Hall until 1841, when they moved to Rownall Hall, Wetley. Sarah’s father, Richard Clarke Hill, who owned Stallington Hall, died in 1853, and the Childs went to live there.
Smith took a keen interest in politics. He was a Conservative. In 1851, he became the Member of Parliament for North Staffordshire and held the seat until 1859.
In 1868, Smith was made a baronet.
He stood for Parliament again. He won the election and was returned to Westminster as the Member for West Staffordshire. A seat he held until 1874, when he retired from politics.
Smith was a philanthropist who took a keen interest in the welfare of disadvantaged individuals. He used his wealth to support local charities that were helping those in need.

He provided financial assistance to the North Staffordshire Infirmary at Etruria and made an annual donation to its general fund. Smith was a member of the hospital’s management committee and served as its president on three occasions. As well as making an annual donation, he contributed to the infirmary’s special funds. The management committee decided to close the infirmary at Etruria and build a new one at Hartshill. It launched a public appeal to raise money to finance the project. A building fund was created, and Smith contributed £1,500. When the Victoria Wards were being erected, he gave £250 towards the cost.
After one of his sons died, Smith built and endowed the Smith Hill Child Memorial Hospital. The hospital, erected in the grounds of the infirmary, was designed to care for patients who were incurable. The infirmary did not have the resources to care for incurable patients, and the project was abandoned. The building was used as a nurses’ home until 1877, when it was converted into a children’s hospital.
In 1875, Smith founded a charity that sent patients who were convalescing to convalescent homes. He endowed the charity with £6,500. The money was invested in securities. The income from these securities was used to send hundreds of men, women and children to seaside convalescent homes.
Smith realised that the pottery industry’s future depended on vocational training.
He was one of the founders of the Wedgwood Institute and organised competitions that awarded prizes to industrial designers. To encourage sales representatives to study foreign languages, he gave prizes to those learning to speak French, German or Spanish.
Although he left Newfield Hall in 1841, Smith retained an interest in Tunstall and its citizens’ welfare. He always referred to people living there as his friends and neighbours.

His first gift to Tunstall was £100, which was given to help finance the construction of Christ Church. He gave £50 when the church appealed for money to build a National School. The appeal was successful, and the school was built in King Street (Madison Street). When St. Mary’s Church launched an appeal to raise money to build a school, he gave £100.
Smith built the church schools in Goldenhill and created a charity to support all church schools in Tunstall and Goldenhill. He helped finance the construction of St. John’s Church in Goldenhill and endowed it with £1,000.
During the 1880s, he made donations to help regenerate Christ Church and St. Mary’s Church. In 1884, he established a workingman’s temperance club at Calver House in Well Street (Roundwell Street).
Six years later, in 1890, he founded the Tunstall Nursing Association. The association was a charity. It employed trained community nurses, who provided free medical care to patients being treated at home.
Tunstall publicly recognised Smith’s generosity in 1893. The clock tower in Market Square (Tower Square) was erected to make sure that he would never be forgotten.
Smith was to ill to attend the tower’s unveiling ceremony. His health continued to decline. He died three years later and was buried in Fulford churchyard
If you and your family worshipped at St. Mary’s or you were at pupil at the school, please use Comments to share your memories with us.
Sir Smith Child (1808-1896) was written by Betty Martin before she died in 2023. More articles she wrote will be posted periodically.
1970s Photographs of Etruria
The area was named by Josiah Wedgewood when he built his new pottery works here in 1769 (it was named after the region of Etruria in Italy in an early example of somewhat fanciful marketing). By the early 1970s, the pottery works had been moved, and the old canal was caught in the doldrums between commercial and leisure traffic.
Note: We viewed Alan’s photographs with great interest and were most impressed by their quality.
During the late 1960s, David photographed the Trent & Mersey and the Caldon Canal for a group of canal enthusiasts opposing British Waterways’ plans to close the canal and turn it into a feeder channel for the Trent & Mersey Canal.
A Polluted Stream at Birchenwood

This image was taken at Birchenwood near Kidsgrove in 1994. It shows a polluted stream. The stream ran next to the route followed by the North Staffordshire Railway Company’s ‘loop line’. The line closed in the 1960s. It ran from Etruria to Kidsgrove. There were stations at Hanley, Waterloo Road, Cobridge, Burslem, Tunstall, Pitts Hill and Goldenhill.
Tunstall’s 18th Century Pottery Industry
Some jasper made at Adams’ Greengates Pottery in Tunstall was equal to, if not superior to, jasper made by Wedgwood at Etruria

William Adams’ Greengates Pottery in Tunstall.
During the 18th century, the Industrial Revolution changed the face of Britain, making it the ‘workshop of the world’.
Earthenware factories were built in Tunstall, a township that included Sandyford, Newfield and Furlong. At the end of the 18th century, there were seven factories making pottery. Small coal and ironstone mines were scattered throughout the district. Blue bricks and tiles were made in the Chatterley Valley.
As early as 1735, William Simpson was making earthenware in the township. By 1750, Enoch Booth had a factory near a field called Stony Croft. The factory made cream coloured ware glazed with a mixture of lead ore and ground flint.
In 1763, Admiral Smith Child built Newfield Pottery, where he produced earthenware. By the 1780s, two brothers, Samuel and Thomas Cartlich, were making pottery and mining coal at Sandyford. There were brick kilns, coal mines, a flint mill and a crate maker’s workshop at Furlong.
During the 1740s, George Booth and his son Thomas leased a pottery factory. on an estate called Will Flats, next to Furlong Lane. In 1779, Burslem pottery manufacturer William Adams rented the factory and part of the estate.
On 1 March 1784, William purchased the factory and the land he had been renting. He changed the estate’s name from Will Flats to Greengates and demolished the old factory.
William built Greengates Pottery (shown above), where he made high-quality stoneware and jasper ornaments for the luxury market. He employed Swiss modeller Joseph Mongolot. Joseph helped him create models for moulds to produce the bas-reliefs for jasper and stoneware.
Pottery produced by William was sold to wealthy customers. Some purchased ware from his showrooms in Fleet Street, London. Others visited the Greengates factory’s showrooms where they bought tea sets, dinner services, jasper, and stoneware ornaments.
In his book, Marks and Monograms on Pottery and Porcelain, William Chaffer mentioned the quality of Adams’ jasper. He said some of it was “equal to, if not superior to” jasper made at Etruria by Wedgwood.
Revised: July 2025